Eyestrain is a common condition that occurs when your eyes get tired from intense use, such as while driving long distances or staring at computer screens and other digital devices. Eyestrain can be annoying. But it usually isn’t serious and goes away once you rest your eyes or take other steps to reduce your eye discomfort. In some cases, signs and symptoms of eyestrain can indicate an underlying eye condition that needs treatment. Now when our eyes work too hard, our eye muscles may contract too much. These contractions can trigger an eye strain headache. Often, these headaches include pain and discomfort behind our eyes too.
Sign of an eye strain headache?
It is important to know how to recognize an eye strain headache. Following are the signs of eye strain headache:
- It develops after a prolonged eye activity like when you focus on something for a long time for say focusing on computer screen, or driving for a long time.
- The pain gets better with rest. The headache gets subside once you rest your eyes.
- Eye strain headache usually does not come with nausea or vomiting.
- It causes pain behind your eyes. The pain is usually located behind and around your eyes. The area might feel tired and sore.
Connection between eye strain and headache:
When we look at some objects or screens at a close range, the muscles in and around our eyes need to work harder to focus. Over time, these muscles can get sore and tired causing head ache.
Symptoms of eye strain headache:
- Sore eyes.
- Watery or dry eyes.
- Temporary double or blurry vision.
- Trouble concentrating.
- Neck, shoulder, or back aches.
- Difficulty keeping your eyes open.
- Sore, tired, burning or itching eyes.
- Sore neck, shoulders or back.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
Causes of eye strain headache:
- Prolonged use of digital screen:
Looking at a digital screen for a long time is the most common cause of eye strain and eye strain headache. In this case, the condition is called digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome. The following scenarios might also worsen digital eye strain:
- Excessive glare or reflection on your screen.
- Low contrast between the screen text and background.
- Digital screens placed at incorrect distances.
- Poor posture of sitting while working.
- Digital eye strain tends to develop more if you look at a screen for 2 or more hours without taking a break.
- Prolonged focus on a single task:
It is not necessary to develop eye strain only using a digital screen for a prolonged period. Your eyes can get tired and have eye strain headache even after continual focus on a single activity for a long time. These include:
- Long-distance driving without a break.
- Reading a book constantly for a long time.
- Working on a project, like sewing or drawing without break.
- Bright or dim lights:
It is difficult to see clearly in light that’s too bright or too dim. We might need to squint our eyes to see. We may have experienced this while driving a car on a sunny day without sunglasses, or walking into a dark room. As our eyes try to focus, they can become tired and strained. If this happens continuously, we can face eye strain headache.
- Vision problems:
Uncorrected vision can also cause eye strain. You might need prescription glasses or contact lenses to help you see things clearly. If you already wear them, you may need a different prescription. If your vision is uncorrected, your eyes will need to work harder to try and form a clear image. This can make your eyes tired and lead to eye strain headaches.
Prevention and precautions of eye strain headache:
- Follow 20-20-20 rule:
Eye strain is commonly caused by doing the same thing for too long with no break. One solution is eye strain exercises like the 20-20-20 rule. Focus on something, other than your current task, that is 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes. This will lower the chance of getting eye strain headache to a great extent.
- Blink often:
Dry eyes can worsen your eye strain symptoms. Blinking often will help moisten your eyes. You can also use artificial tear drops to help prevent dry eyes.
- Position your screen in the right way:
Make sure you’re looking at your digital device at the correct distance and in the proper position. The screen should be a few feet away from your eyes, or about arm’s length. You should view the screen at the level of your eyes or slightly below them. This goes for handheld digital devices too. They should be used at below eye level. Also, enlarge the text on the screen to best suit your comfort level.
- Avoid using screens in the dark:
Your eyes will need to work extra hard to focus in the dark. The light from your screen should be similar to the light in the room to make it easier to your eyes and avoid eye strain.
- Find the right light:
Lighting can cause eyestrain or eyestrain headache. Light should come from behind you if you’re focusing intensely on something like reading. Dimming the lights may help reduce eyestrain when watching TV. Make sure the screens that you’re viewing are adequately lit as well. Adjust the brightness as needed. Glare can contribute to eyestrain, so try shading windows or using filters to reduce glare on your digital device.
- Reduce time on a single activity:
A simple way to avoid eyestrain is to limit the time you’re exposed to a single activity that requires intense focus. Try to spend less time on digital devices or at least take breaks in between your work.
- Avoid prolonged use of contact lenses:
Wearing contact lenses for a prolonged period can cause eye irritation and eyestrain.
Complications from Eyestrain:
- Problems in retina like retinal infections.
- Cataracts.
- Age-related macular degeneration.
- Disturbance in sleeping.
Treatments of Eyestrain Headache:
Home Treatments and Care:
- Simply resting your eyes for several minutes can give you relief. Just close your eyes and better take a nap.
- Dryness can make your eye strain worse. Using artificial tears may help moisten your eyes and offer relief.
- Apply a warm, wet washcloth to tired eyes to get a relief.
- If you have a stubborn eye strain headache, an over-the-counter Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)may help.
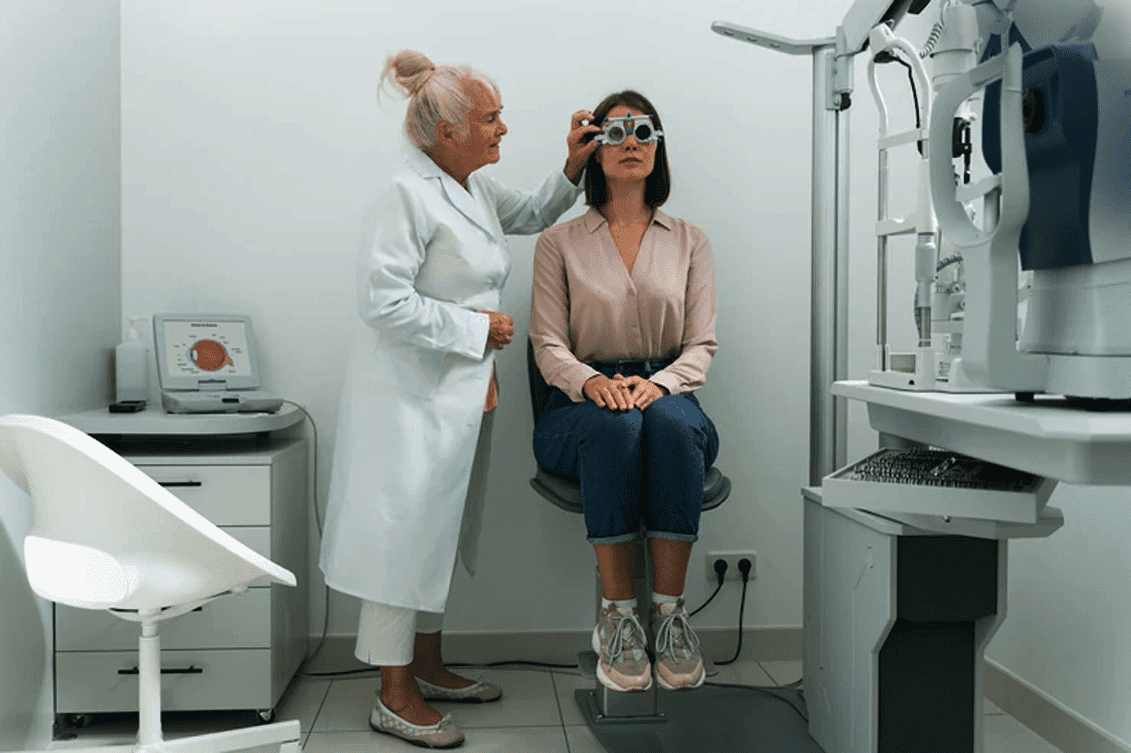
When to see the Doctor:
You should visit the doctor if you face same issues even after taking the preventative measures and you go through the headache even after a good sleep.
Along with, if you face the following symptoms along with eyestrain headache, visiting the doctor is a must:
- Sudden vision changes.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Severe eye pain.
Natural Medication for preventing Eyestrain headache:
Some eyestrain symptoms may be relieved by natural products or medicines, such as bilberry extract and omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil. But further study is needed. It is better to consult with your doctor if you are considering supplements or natural medicines to help relieve your signs and symptoms of eye strain or eye strain headache.
Myths about Eyestrain Headache:
- Digital eye strain does not affect people who wear corrective eyewear.
- There is no treatment for digital eye strain.
- Digital eye strain does not affect work productivity.
Eye strain headache is not that worst eye problem but ignoring it can be worst. Eyes is something which is very vital for our working life and even day to day life. When eyes help us to work, it is our responsibility to take good care of our eyes while working, especially while working in digital screens by taking breaks in between works, giving them rest by taking short naps and proper sleep (7-8 hours) at night. There is an increases prevalence of Eyestrain headache among children in COVID era. Parents should be considerate about duration, type and distance of digital device use to avoid Eyestrain in children. Online classes are still going on in many schools. The school authorities should take care of the fact and should give breaks to the students in between every classes.
This also need to be included that most headaches are not due to eye strain. Some are tension-type headaches that have little to do with vision. Headaches that are present on awakening or those that wake one from sleep also are not caused by eyestrain. Additionally, eyestrain headaches are not generally associated with nausea or vomiting. For the vast majority of people with headaches, making changes to their glasses, using prisms, doing eye exercises and other types of “vision therapy” are generally not useful. Instead, these people have what is called a primary headache disorder, and these headaches are not related to visual concerns at all. The two most common primary headache disorders are migraine and tension-type headache. It is always better to see a doctor if the problem is prolonged and also if you cannot figure out what problem you are going through.